|
Ordering information |
|||
|
Name |
Cat. No. |
Vol. |
Scheme |
|
G-IA |
PMG041-2 |
2 ml |
|
1. Overview
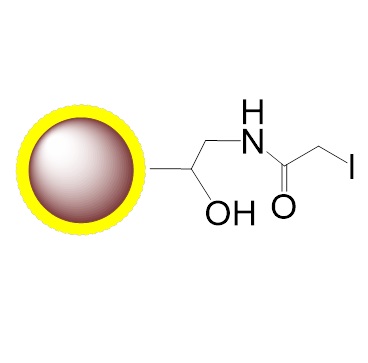
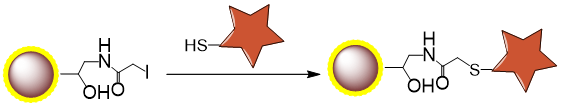
PuriMag™ G-IA, Iodoacetyl-Activated Magnetic Nanoparticles are uniform, polymer-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Their hydrophilic surface ensures excellent dispersibility, low non-specific adsorption, and easy handling in diverse buffers. The beads feature a high-density surface coating of iodoacetyl functional groups, designed for covalent coupling with thiol (-SH) containing ligands.
Optimized for conjugating large proteins and small peptides, the hydrophilic spacers minimize steric hindrance. Post-coupling rigorous washing eliminates non-specifically bound proteins, while the unique surface chemistry provides:
Ultra-low background binding in protein-based systems
Superior handling without surfactants
Versatility for research/diagnostic applications (lab-scale to high-throughput)
Features & Advantages:
Covalent, specific binding to cysteine residues
Solvent Compatibility: Water-insoluble ligands coupled in:
10–30% acetonitrile, DMF, or DMSO; or
6 M Guanidine HCl
Stable covalent bonds with minimal ligand leakage
Generates reusable immunoaffinity matrices
Low non-specific binding
Capacity: 1–20 mg protein or 0.1–2 mg peptide per gram beads
Applications: Antibody/protein/peptide/DNA/RNA purification; cell sorting; immunoprecipitation
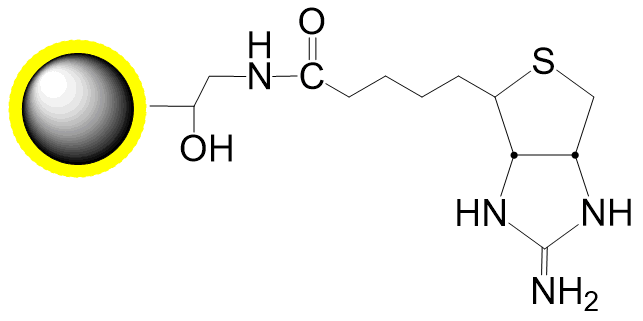
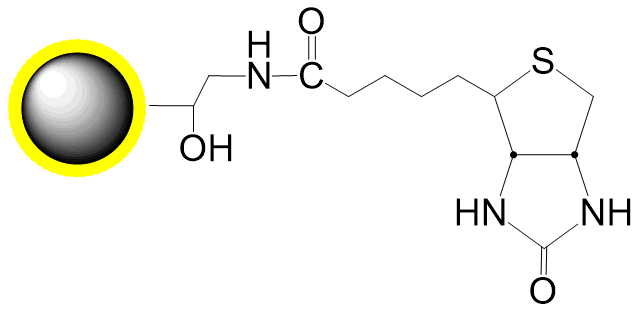
Schematic Diagram of Thiol Coupling Mechanism:
2. product description
Product Specifications
Description
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Particle Size
200 nm
Number of Beads
~1.7×1010 beads/mg
Matrix
Proprietary polymer
Functional group
Iodoacetyl groups
Group density
~300 µmole / g of Beads
Magnetization
60~70 EMU/g
Formulation
10mg/mL in in 1M NaCl and 0.02% NaN3
Stability
pH 3.5~10, 4~50 ℃, most organic solvents
Storage
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze.
3. Instructions for Use
Note: The following protocol exemplifies coupling proteins/peptides to PuriMag™ G-IA Iodoacetyl-Terminated Magnetic Beads. Strong titration-based optimization of bead quantity for each application is recommended. Scale proportionally as needed.
A. Required Materials
1.Magnetic Racks (manual operation):
For 12×1.5–2 mL tubes (Mrack02)
For 2×50 mL or 2×15 mL tubes (Mrack03)
2.Coupling Buffers:
Soluble Ligands: 50 mM Tris, 5 mM EDTA-Na, pH 8.5
Insoluble Ligands: 50 mM Tris, 5 mM EDTA-Na, pH 8.5, containing:20–30% DMSO or DMF or 6 M Guanidine•HCl
3.Wash Solution: 1 M NaCl in distilled H₂O
4.Blocking Compound: L-Cysteine•HCl
5.Reducing Agent: TCEP (Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine)
6.Dilution Buffer: Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
B. Sample Preparation
Critical Pre-treatment:
Ensure proteins/peptides contain free (reduced) thiol groups.
Reduce disulfide bonds using:
DTT (Dithiothreitol)
TCEP (Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine)
2-MEA (2-Mercaptoethylamine•HCl)
Remove reductants via desalting/dialysis post-reduction.
Special Cases:
-
Newly synthesized peptides: Use directly if reduced thiols are confirmed.
-
Proteins: Treat with 5–10 mM TCEP (RT, 30 min) → desalt/dialyze.
-
IgG antibodies: Prefer 2-MEA for selective hinge-region disulfide reduction.
-
Avoid residual reductants (e.g., 2-mercaptoethanol, DTT, TCEP) in samples.
Procedure:
1.Dissolve 1–10 mg protein/peptide in 1 mL coupling buffer (soluble or insoluble formulation).
2.If pre-suspended in other buffers, dilute with equal volume coupling buffer.
C. PuriMag™ Bead Preparation
1.Transfer 3 mg beads to centrifuge tube. Resuspend in 100 μL coupling buffer. Vortex vigorously for 1–2 min.
Note: Use hydrated beads immediately due to functional group instability. If aggregated, disperse via vigorous vortexing or gentle ultrasonication (10–30 sec).
2.Perform magnetic separation, discard supernatant. Remove tube from stand. Resuspend in 1 mL coupling buffer by vortexing for 30 sec.
3.Repeat Step 2 once.
D. Coupling
1.Add sample (from B.1/B.2) to washed beads. Incubate with gentle rotation at RT for 30–60 min.
2.Wash beads 4× with 1 mL coupling buffer (as in C.2).
3.Block excess reactive groups by suspending beads in 1 mL coupling buffer with 8 mg L-Cysteine•HCl. Incubate at RT for 30–60 min.
4.Wash beads 4× with 1 mL wash buffer (as in C.3).
5.Resuspend in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. Store at 4°C.
E. General Affinity Purification Protocol
Note: While nucleic acid purification is relatively straightforward due to biochemical consistency, protein purification requires application-specific optimization.
1.Transfer optimized bead amount to a centrifuge tube. Perform magnetic separation for 1–3 min. Discard supernatant.
Note: Titrate beads against target protein abundance in crude samples. Typical yield: 1–20 μg target protein per mg beads. Excess beads increase background; insufficient beads reduce yield.
2.Resuspend beads in 5 bead volumes PBS for 30 sec. Separate magnetically (1–3 min). Discard supernatant.
3.Repeat Step 2 twice (total 3 washes).
4.Add washed beads to crude sample containing target protein. Incubate 1–2 h at RT or optimized temperature (longer for lower temperatures).
5.Wash with PBS or 1M NaCl until eluate OD₂₈₀ ≤ 0.05 (background level).
6.Elute target protein using:
Low pH (2–4)
High pH (10–12)
High-salt buffer
Heat denaturation
Affinity elution
Boiling in SDS-PAGE loading buffer
(For research use only!)