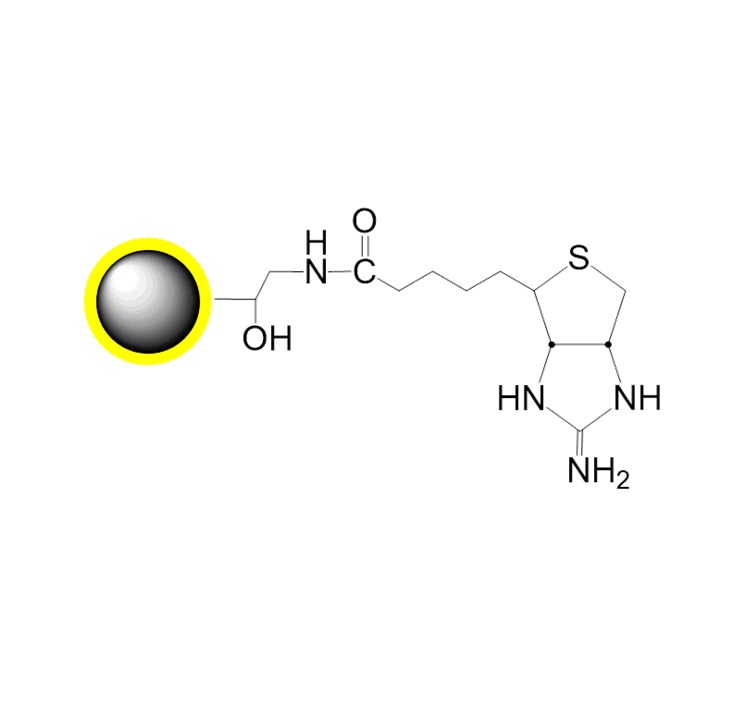
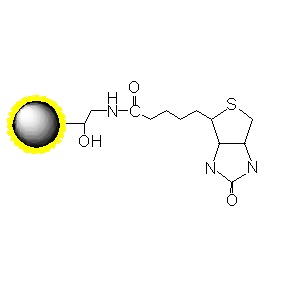
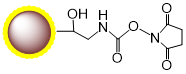Ordering information
Name
Cat. No.
Vol.
Scheme
G-NHS
PMG009-2
PMG009-5
2 ml
5 ml
1. Overview
PuriMag™ G-NHS Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles are uniform, polymer-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Their hydrophilic surface ensures excellent dispersibility in various buffers, low non-specific adsorption, and easy handling. The surface is coated with a high density of NHS (N-Hydroxysuccinimide) functional groups for permanent covalent coupling to primary amine-containing ligands. Other active groups in the ligands require no protection prior to coupling. Coupling occurs rapidly (15-30 min at RT, pH 6.5-9.0 or 4 hr at 4°C). PuriMag™ G-NHS beads are optimally suited for conjugation with both large proteins and small peptides.
NHS-Bead Conjugation Mechanism:
[Illustration concept translated]
The NHS ester on magnetic beads reacts with primary amines (-NH₂) on ligands (proteins/peptides) to form stable amide bonds, releasing N-hydroxysuccinimide.

2. product description
Product Specifications
Description
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Particle Size
200 nm
Number of Beads
~1.7×1010 beads/mg
Matrix
Proprietary polymer
Functional group
NHS group
Group density
~300 µmole / g of Beads
Magnetization
60~70 EMU/g
Formulation
10 mg/ml suspension in Acetone
Stability
pH 3.5~10, 4~80 ℃, most organic solvents
Storage
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze.
3. Instructions for Use
Notes:
1.The following protocol exemplifies coupling amine-containing ligands to PuriMag™ G-NHS activated magnetic beads. Titration is strongly recommended to optimize bead quantity for each application. This protocol can be linearly scaled up or down.
2.Ionic strength of the coupling buffer is critical for achieving higher coupling efficiency.
3.Coupling buffer should have minimal ionic strength and must not contain any amine groups (e.g., Tris). Wash or storage buffers may contain amines or carboxyl groups.
A. Required Materials
1.Magnetic rack (for manual processing):
Compatible with 12 individual 1.5-2 mL microcentrifuge tubes
Compatible with 2 × 50 mL or 2 × 15 mL centrifuge tubes
2.Coupling Buffer: 10 mM Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 5.5
*(Note: pH 6.5-9.0 may be used, but optimal coupling efficiency is achieved at pH ~5.5)*
3.Wash Buffer: 0.05 M Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, pH 8.0
4.Blocking Buffer: 1 M Ethanolamine, pH 9.0
B. Protein Conjugation Protocol
1.Weigh and transfer 30 mg magnetic beads to a centrifuge tube.
2.Dissolve 0.5-1 mg protein/peptide in 1 mL Coupling Buffer.
*Note: Coupling efficiency of NHS-activated beads varies by ligand. Users should empirically optimize ligand concentration. Recommended protein concentration: 0.5-10 mg/mL. For small peptides, use ≥200 μmol ligand per mL.*
3.Add protein solution to beads. Resuspend beads and mix thoroughly by pipetting or vortexing. Incubate with continuous rotation for 4-6 hr at RT or overnight.
4.Place tube on magnetic separator for 1-3 min. Remove supernatant while tube remains on separator. Take tube off separator and resuspend beads in 1 mL Wash Buffer by vortexing for 30 sec. Magnetically separate and remove supernatant.
5.Wash beads 3-4 times with 1 mL Wash Buffer (or 1 M NaCl) as described in Step 4.
6.Add 0.5-1 mL Blocking Buffer to beads (alternative blocking: PBS, pH 7.4 with 0.1% BSA). Incubate 1 hr at RT or overnight at 4°C.
7.Wash beads 3 times with 1 mL cold Wash Buffer as in Step 4.
8.Resuspend beads in PBS (pH 7.4) containing 0.1% BSA and 0.1% sodium azide (w/v) to desired concentration. Store at 4°C. DO NOT FREEZE.
Appendix:
Immobilization of Small Molecule Compounds in Organic Phase Using NHS Magnetic Beads
1. Materials
PuriMag™ Beads & Ligand
NHS magnetic beads: 10 mg (Functional groups: 200–300 nmol/mg)
Storage: In isopropyl alcohol
Compound: ~1 mg
*Note: NHS beads stored >1 month exhibit reduced binding capacity*
Reagents
N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF)
2-Aminoethanol (Ethanolamine, M.W. 61.08)
Methanol
Ammonium acetate (M.W. 77.08)
Acetic acid (M.W. 60.05)
Acetonitrile
Equipment
Centrifuge
Vortex mixer
Rotator
Ultrasonic disperser
Magnetic rack
HPLC system (Waters 2695 with 2998 PDA and SMH detector)
HPLC column (Waters Symmetry 5μm C18 4.6×250mm, WAT054275)
2. Methods
2.1 Compound Immobilization on NHS Beads
1.Prepare 5 mM compound solution in DMF
2.Aliquot 2.5 mg NHS beads per immobilization concentration
*(Beads suspended in isopropyl alcohol)*
3.Wash beads with DMF (magnetic separation at RT, discard supernatant)
4.Suspend beads in specified DMF volume, add 5 mM compound solution as below:
|
Concentration of compound at immobilization (mM) |
0 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
1 |
|
DMF (μl) |
500 |
490 |
470 |
400 |
|
5 mM compound solution (μl) |
0 |
10 |
30 |
100 |
5.Mix on vortex mixer at RT for 70 min
6.Magnetically separate at RT
7.Transfer supernatant (Sup A) to new tube for HPLC analysis (released NHS)
8.Resuspend in 500 μL 1M ethanolamine in DMF (using rotator)
9.Mix on vortex mixer at RT for 2 hr
10.Magnetically separate at RT
11.Transfer supernatant (Sup B) to new tube for HPLC analysis (released NHS)
12.Wash 3× with 500 μL 50% methanol/water
13.Resuspend in 100 μL 50% methanol/water (using rotator), store at 4°C
2.2 Quantification of Immobilized Compound
1.Prepare 10 mM ammonium acetate (pH 5.70)
2.Prepare sample buffer & standards:
*Sample buffer: 47 mL 10 mM ammonium acetate + 3 mL acetonitrile (94:6)*
*Standards: 0, 10, 100, 1000, 5000 μM NHS in DMF*
3.Mix 20 μL standard/Sup A/Sup B with 180 μL sample buffer
4.Filter through 0.2 μm centrifugal filter at 5,000 × g for 1 min
5.Load 150 μL filtrate to HPLC autosampler
6.HPLC conditions:Gradient (40 min total, includes column wash):
|
Time (min) |
10 mM ammonium acetate (%) |
Acetonitrile (%) |
Gradient curve |
|
0 |
94 |
6 |
|
|
10 |
60 |
40 |
Linear |
|
12 |
20 |
80 |
Linear |
|
20 |
20 |
80 |
Linear |
|
22 |
94 |
6 |
Linear |
|
40 |
94 |
6 |
Linear |
-
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
-
Injection volume: 50 μL
-
Temperature: 40°C
-
Run HPLC, quantify NHS from peak area at 260 nm
-
Calculate:
-
Immobilized compound = NHS in Sup A
-
Carboxyl groups on beads = NHS in (Sup A + Sup B)
-