|
Ordering information |
|||
|
Name |
Cat. No. |
Vol. |
Scheme |
|
G-DADPA |
PMG043-2 |
2 ml |
|
1. Overview
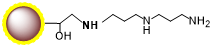
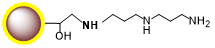
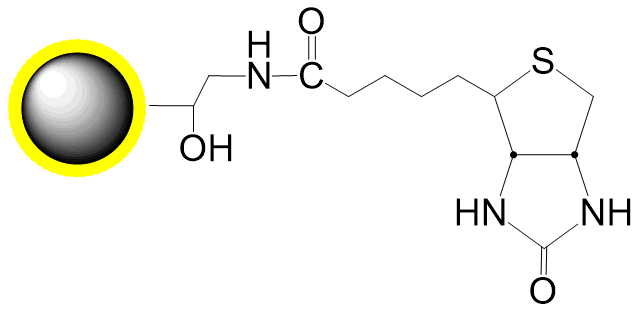
PuriMag™ G-DADPA Activated Magnetic Nanoparticles are uniform, superparamagnetic beads with a hydrophilic polymer coating. The surface features a high density of DADPA (Diaminodipropylamine) functional groups.
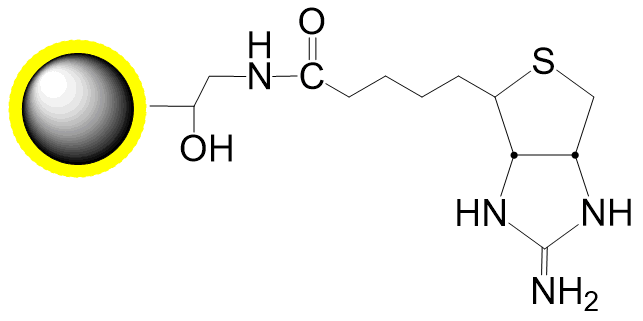
Small molecules such as steroids, dyes, and pharmaceuticals often lack reactive groups (e.g., primary amines, thiols, carbonyls), making conventional immobilization challenging. However, compounds with active hydrogens can be covalently fixed to DADPA-terminated beads via the Mannich reaction through condensation with formaldehyde and amines. PuriMag™ G-DADPA beads enable immobilization of active-hydrogen-containing steroids, drugs, and chemical compounds for affinity purification.
Features & Advantages:
Coupling Reaction Equation:
High binding capacity
Rapid, efficient coupling
Hydrophilic long-arm spacers minimize steric hindrance and non-specific binding
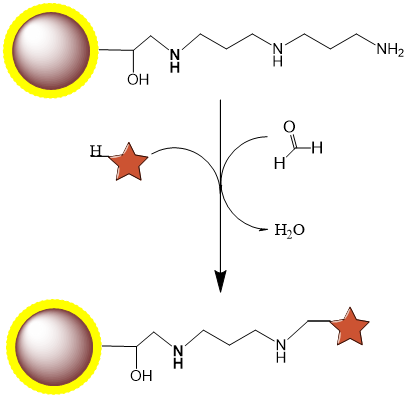
2. product description
Product Specifications
Description
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Particle Size
200 nm
Number of Beads
~1.7×1010 beads/mg
Matrix
Proprietary polymer
Functional group
DADPA group
Group density
~300 µmole / g of Beads
Magnetization
60~70 EMU/g
Formulation
10 mg/ml suspension in 50% acetone
Stability
pH 3.5~10, 4~80 ℃, most organic solvents
Storage
1 year at 4~8 ℃. Do not freeze.
3. Instructions for Use
Note: This protocol exemplifies coupling amine-containing ligands to PuriMag™ G-DADPA-Terminated Magnetic Beads. Titration-based bead optimization is strongly recommended. Scale proportionally. Coupling buffer/ligands must exclude amines (e.g., Tris) or formyl groups to prevent solution-phase polymerization and low efficiency.
A. Required Materials
1.Magnetic Racks:
For 12×1.5–2 mL tubes (Mrack02)
For 2×50 mL or 2×15 mL tubes (Mrack03)
2.Coupling Buffer: 0.1 M MES, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 4.7
3.Wash Buffer: 0.1 M Tris, pH 8.0
4.Coupling Reagent: 37% Formaldehyde
B. Coupling ProcedureB-1. Sample Preparation
Soluble ligands: Dissolve 1–10 mg ligand in 1 mL coupling buffer.
Insoluble ligands: Dissolve in 0.5 mL 100% ethanol, then add 0.5 mL coupling buffer (50% ethanol/buffer).
*Note: For ethanol-based coupling, pre-wash beads with 50% ethanol.*
B-2. Bead Preparation
1.Transfer 10 mg beads to microcentrifuge tube.
2.Place tube on magnetic stand for 1 min. Discard supernatant. Resuspend in 1 mL coupling buffer.
3.Repeat Step 2 three times (total 4 washes).
B-3. Coupling
1.Add prepared sample + 100 μL 37% formaldehyde to washed beads. Mix thoroughly. Incubate with continuous rotation at 38–60°C for ≥48 h.
Note: Optimize time/temperature empirically.
2.Wash beads:
Standard: 4× with 1 mL coupling buffer → 2× with H₂O.
For ethanol-coupled ligands:
3× with 50% ethanol
2× with deionized H₂O
2× with 100% ethanol
2× with deionized H₂O
3.Resuspend in storage buffer with 0.05% NaN₃. Store at 4°C.
C. General Affinity Purification Protocol
1.Transfer optimized bead amount to centrifuge tube. Perform magnetic separation for 1–3 min. Discard supernatant.
Note: Titrate beads against target protein abundance. Typical binding: 1–20 μg target protein per mg beads. Excess beads increase background; insufficient beads reduce yield.
2.Wash beads 3× with 5 bead volumes PBS:
Remove tube from magnet.
Resuspend in PBS for 30 sec.
Separate magnetically (1–3 min). Discard supernatant.
3.Incubate washed beads with crude sample containing target protein at RT or optimized temperature for 1–2 h (extend for lower temperatures).
4.Wash with PBS or 1M NaCl until eluate OD₂₈₀ < 0.05.
5.Elute target using:
Low pH (2–4)
High pH (10–12)
High-salt buffer
Heat denaturation
Affinity elution
Boiling in SDS-PAGE loading buffer
(For research use only!)
*Note: Store beads as 10 mg/mL suspension in 20% ethanol/water at 4°C. Vortex before use.*
Note: Protein purification requires application-specific optimization due to structural diversity.